We are going through a period characterized by two ongoing wars, interest rates higher than the last 20 years and a level of inflation (which despite the recent decline) remains sticky, but despite everything the global stock markets are preparing to close the month of November with a vigorous rally.
And what’s happening to volatility? These critical issues do not effect it at all. These remain well below the alert levels. Continue reading this guide to learn about Vix and how it works.
What are Vix and VSTOXX?
The Vix Index is an index calculated by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) to measure implied market volatility expectations over the next 30 days.
The Vix is calculated by taking as a reference the weighted prices of 30-day put and call options on the S&P 500 index. Therefore attempts to measure the volatility (i.e. price fluctuations) of the S&P 500. The index follows the performance of the 500 American companies with the largest capitalization.
Key Points About the VIX
Read the key points in the below section.
Measurement
Investors therefore analyze the trend of the Vix to measure the level of risk on the stock market. Due to this nature the Vix index mostly people also refer it to the fear or market stress index. But the Vix is not the only indicator of market sentiment.
In fact, to measure price fluctuations on the European stock exchange, investors can also analyze the more specific VSTOXX, an index that measures the expected volatility on the European market, but in this case taking the EuroStoxx 50, the index of 50 blue chips, as a reference Europeans.
Market Sentiment
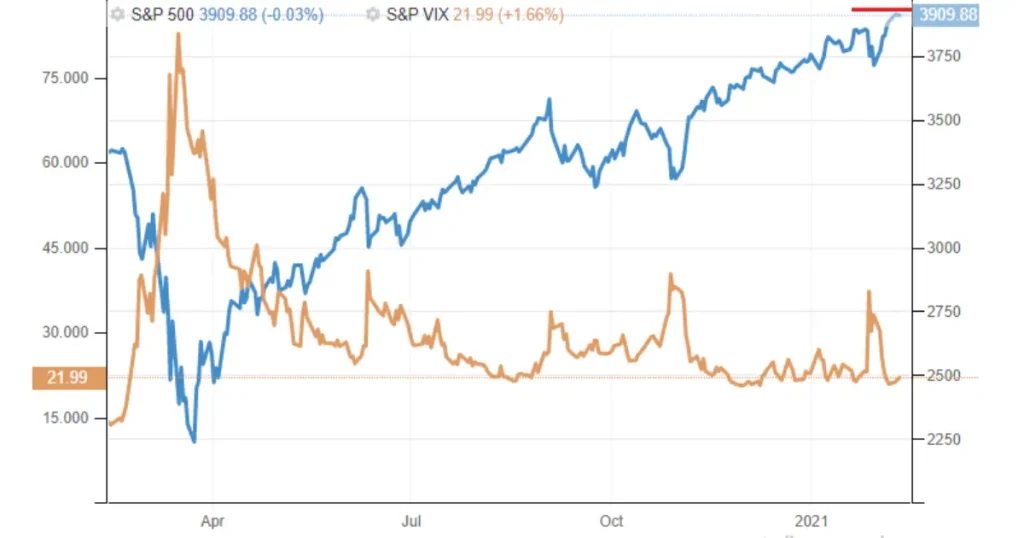
The case of the Covid crisis was emblematic, with the VIX reaching over 60 points, when the psychological threshold of fear and tension is generally represented by 30 points. Basically, in fact, the higher the VIX, the greater the perception of risk present on the market and the greater the volatility expected by investors in the following month. The levels to monitor carefully with regards to the VIX are close to 30 points: when the index is above this value, operators typically expect volatility and, generally, declines on the stock market.
A value below 20 points of the VIX indicates a phase of tranquility on the stock markets, where there is a lot of confidence and the bullish phase is well set up, with operators not needing to hedge. Currently, the term structure of the VIX, i.e. the value of the various VIX futures contracts reported based on the futures’ expiries themselves, is comforting in the short term, but still close to 30 points.
In fact, operators, looking at the structure and term of the VIX, expect a reduction in implicit volatility between November and December and then return to an increase in volatility in the first half of 2023. By June 2023 the tension should ease, also thanks to the stop of aggressive monetary policies by the FED.
How to Use the VIX?
The instruments that derive their value from the VIX are very complex and as such should be handle with care. Instruments that derive their value from the trend of the VIX are mainly by expert traders for hedging or speculation purposes. Long US stock traders buy the VIX, using specific derivative instruments, to hedge against any unexpected short-term declines and sell the VIX when they expect a reduction in volatility and a rise in the markets.
There are also ETFs that replicate the performance of the VIX index, but these instruments will suffer from the problem of contango in the next two months. Contango is the situation in which future prices (expressed by futures) are higher than the current stock price (by the spot price). So that the forward curve is upwards.
When the term structure is in contango, investors pay a premium for holding the position: as a result, an investment using futures automatically decreases in value. The term structure of the VIX is in contango for the next two months and in backwardation (the opposite of contango) for January, February and March.
Why Do We Have to Use a VIX Above 30 Points?
As the term structure of the VIX shows, in the coming months this index is expected to remain steadily close to the fear threshold, i.e. 30 points. The uncertainty resulting from inflation persistently above the central banks’ target level (2%) and the continuation of the Russia-Ukraine conflict make the short-term scenario anything but calm for the real economy and for investments of a financial.
The volatility index (VIX), which measures anxiety, also confirms the lack of clarity about the near and medium term. It could remain above 30 points until there is a decisive slowdown in inflation and a stop to the rate increases implemented by the central banks to contain it.
Looking only at the VIX index, without understanding where the macroeconomic cycle is available, is not a sensible strategy for the long-term investor. On the contrary, the VIX must be an important support tool for the investor in order to optimize his strategic asset allocation.
In a phase like the current one, where the stock and bond markets have fallen significantly from their highs and where uncertainty reigns supreme, it makes no sense to interrupt one’s existing accumulation plans or disinvest: an investor with a well-designed portfolio in financial instruments efficient does not have to fear potential short-term fluctuations, taking advantage of every decline to accumulate and continue with the set strategy.
Vix in 2024
Big investors want toapproach 2024 without shocks, therefore at the current price levels, or little more. Yesterday, the Vix closed trading at 12.50 points, slightly higher than last week’s lows of 11.81 points, levels not seen since 2020, highlighting this pattern clearly.
The index that calculates the implicit volatility of the stock market The USA has now been in a lateral-descending channel for a month, well below the warning level indicated above 20 points. The trend seems oriented towards continuing the current decline, towards last week’s lows. Statistically, a Vix reading below 12 points implies an average daily movement of the S&P 500 of just 0.75%, and an average weekly movement of just 1.7%.
A picture that perfectly reflects the current market situation with American indices slowly moving upwards. The market-moving institutional investors appear to have come to an informal understanding: do not make any hasty decisions before year’s end lest you jeopardize the stellar performance of 2023, upon which your bonuses will be based.
A situation that however cannot last forever. The median value of the Vix index hovers around the threshold of 20 basis points and statistically, since its measurement began in 1990, the index has had a price below 12 points for only 10% of its time. For these last sessions of the year it may still be fine, but already in the first weeks of 2024 the music could change.
Traders are being a little too confident in pricing in the best-case scenario in which inflation cools, the Fed starts cutting borrowing costs and the economy is able to avoid a long-overdue recession. This is certainly a possible scenario but, for it to materialize, the economic data in the coming months will not have to record sudden movements. Meanwhile the Vix is always ready to rebound.