Many people don’t realize that a single open RDP port can invite hackers straight into their system. Remote Desktop makes it easy to manage computers from anywhere, but if it’s not secured, it becomes a serious risk.
Cybercriminals often scan for the default RDP port, 3389, looking for weak points to attack. Therefore, it is necessary to understand how RDP network ports work, why leaving the default one open is dangerous, and how to change it safely.
In this blog, you’ll also learn how to secure your remote access and protect your network from unauthorized connections. Let’s make your RDP setup safer and more reliable.
What Is An RDP Port?
An RDP port allows one computer to connect to another remotely. It uses the Remote Desktop Protocol, developed by Microsoft. This protocol helps users control another device through a network. The RDP port works like a communication gateway between systems.
By default, it uses port 3389 to send and receive data. When a remote session starts, the port transfers screen visuals and user inputs. It allows IT teams and users to manage systems without being physically present.
How Does RDP Use Port 3389?
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) uses port 3389 for communication between devices. This port allows remote connections over a network. When you use RDP, your computer connects through this port to another system.
Communication Process
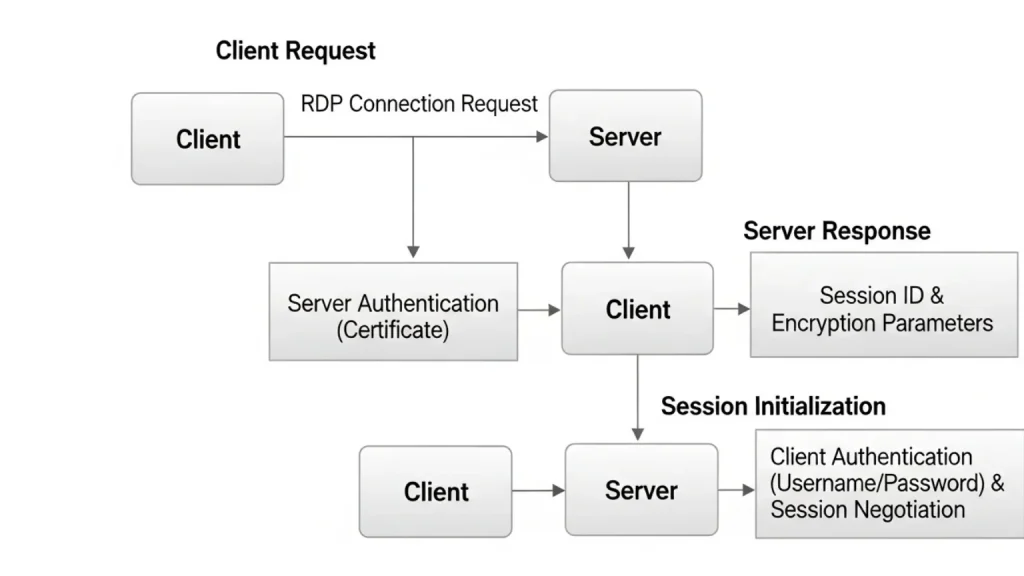
The communication starts when a client sends a request through port 3389. The data travels using TCP/IP. RDP encrypts this data to keep it private. The communication process consists of three main steps.
- Client Request: When you open Remote Desktop, your device acts as a client. It sends a signal to the target computer using port 3389. The client also shares login details for verification.
- Server Response: The server receives the request and checks the login credentials. If they match, the server grants access. It then sends configuration data back to the client. This includes screen settings, session details, and user permissions.
- Session Initialization: After authentication, the session starts. The user can now see and control the remote desktop. The client displays the server’s desktop in real time. All actions are transmitted securely through port 3389.
How To Change RDP Port Listening From 3389
Changing the default RDP port can help protect your system from attacks. Follow these steps carefully to change the port.
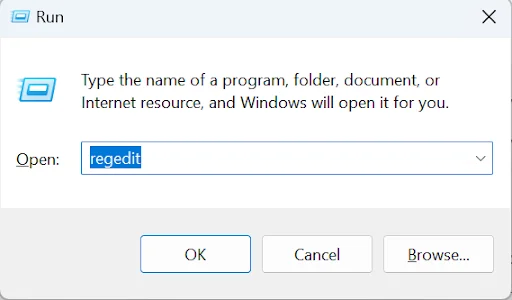
1. Open Registry Editor
Press Win + R, type regedit, and press Enter.
2. Go to RDP Settings
Navigate to: “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp”
3. Locate the PortNumber
In the right pane, find the PortNumber entry.
4. Change the Port
Right-click PortNumber, select Modify, and set the Base to Decimal. Type your desired port, for example, 3390, then click OK. Avoid using ports reserved for other services, especially below 1024.
5. Restart the Computer
Close the Registry Editor and restart your PC to apply the new port.
6. Update Firewall Settings
Open Windows Defender Firewall or your Windows firewall tool. Add a new inbound rule for TCP traffic on the new port. Update your router or other firewalls if necessary.
7. Test the Connection
Use your RDP client to connect with the new port: “hostname_or_IP:3390”
Are There Other Ports For RDP?
RDP primarily uses port 3389, but you can change it or use alternative ports for security or custom setups. Below is a table showing other ports that can also support Remote Desktop Protocol.
| Port Number | Purpose | When It’s Used |
| 3389 (Default) | Default RDP port for Windows systems. | Used for standard remote desktop connections. |
| 3390 | Custom port for RDP. | When users change the default port to reduce attacks. |
| 3388 | Alternate RDP port. | Used in environments running multiple RDP servers. |
| 443 (HTTPS) | Secure RDP through an SSL tunnel. | Used when RDP is routed via secure HTTPS. |
| 22 (SSH) | Used for tunneling RDP through SSH. | Common in Linux or secure network setups. |
What Are The Main RDP Security Issues?
RDP offers easy remote access, but it also opens doors for hackers. Common threats include the issues discussed below.
Unsecured Ports
Leaving RDP ports open makes your network vulnerable. Attackers can scan and exploit them easily. The default port, 3389, is a popular target. Change it to a non-standard port to reduce risk. Always use a firewall to limit who can connect and monitor incoming traffic for suspicious activity.
Credentials Theft
Weak or reused passwords are a hacker’s dream. Cybercriminals use brute-force attacks to guess login details. Once they gain access, they can steal sensitive data. Use strong passwords, enable multi-factor authentication, and avoid sharing credentials.
Server Exploits
Outdated servers often have vulnerabilities. Hackers can use these flaws to take control of your system. Regular patching helps fix known issues. Keep your operating system and RDP client updated. It’s a powerful way to prevent unauthorized access and maintain server security.
Protocol Tunneling
Attackers may hide malicious activity by tunneling RDP traffic. This makes it harder to detect intrusions. To prevent it, use VPNs or secure gateways for remote access. They encrypt data and block unauthorized tunnels.
Session Hijacking
During an active RDP session, hackers can intercept and take control. This often happens when encryption is weak. Always use the latest RDP version with strong encryption. Limit session access and log out when not in use.
Ddos Attacks
Hackers can flood your RDP server with fake traffic, causing downtime. These attacks disrupt access and drain resources. Use firewalls, rate limiting, and intrusion detection systems. They help filter malicious traffic. Consistent monitoring ensures your remote access remains stable and secure.
How To Secure RDP Port?
- Use Strong Passwords: Always create complex passwords for RDP accounts. Avoid common words or patterns.
- Enable Network Level Authentication (NLA): NLA ensures users authenticate before connecting. It adds an extra layer of security.
- Limit RDP Access by IP: Only allow trusted IP addresses to connect. This reduces exposure to attacks.
- Change the Default RDP Port: Switching from port 3389 makes it harder for hackers to find your RDP.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): 2FA adds a second verification step, preventing unauthorized access.
- Keep Systems Updated: Regularly update Windows and software to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor RDP Logs: Check connection logs for suspicious activity. Respond quickly to unusual attempts.
What Port Ranges Can Be Used for RDP?
RDP sometimes uses TCP and UDP ports to connect a client to a host. The default port is 3389. You can change it for security or network needs. Always pick a port that is free and not used by critical services.
| Range | Port Numbers | Description |
| Well-known ports | 0–1023 | Reserved for system services like HTTP, SSH, FTP |
| Registered ports | 1024–49151 | Safe for user-defined services, including RDP |
| Dynamic/Private ports | 49152–65535 | Temporary or private ports, suitable for custom RDP |
Tips for Choosing Alternative RDP Ports
- Avoid common ports like 80, 443, 21, and 22.
- Use ports near 3389, such as 3390, 3391, or 3395.
- Dynamic range ports, like 50000, 55000, or 59999, reduce visibility to scans.
- Always check that the port is free and allowed in firewall rules.
- Document changes clearly for all users and admins.
Closing Insights on RDP Configuration
Changing your RDP port is like giving your system a secret door. Hackers scanning the default 3389 port won’t even know your new entry point exists. It’s a small tweak, but it makes a big difference in security. Just edit the registry, update your firewall, restart, and you’re good to go.
You can also learn in detail about the Windows Modules Installer Worker to keep your system working smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, a restart is necessary for the new port setting to take effect. Without restarting, RDP may continue using the old port, and the change won’t work.
Changing the default port makes your system less visible to automated attacks targeting port 3389. It does not replace other security measures, but it adds an extra layer of protection.
If you use port forwarding to access RDP from outside your network, you must update the router settings. For local network connections, router changes are not required.










