Data is everywhere, but turning data into decisions is where the real magic happens.
From Netflix recommending your next binge-watch to businesses predicting customer behavior, Data Science is the driving force behind many of today’s smartest technologies.
But what exactly is Data Science? Is it only for programmers? And how can someone build a career in this fast-growing field?
In this guide, you’ll learn what Data Science really means, how the career path works, which tools professionals use daily, and how Data Science is applied in real-life industries like healthcare, finance, marketing, and AI.
What is Data Science?
Data Science is a field that focuses on collecting, analyzing, and interpreting large amounts of data to discover useful insights and support better decision-making.
It combines skills from mathematics, statistics, programming, and domain knowledge to turn raw data into meaningful information. Data scientists use tools and techniques such as data analysis, machine learning, and visualization to identify patterns, predict future trends, and solve real-world problems.
The Data Science Workflow
Every data science project follows a similar path, though rarely in a straight line:
Problem Definition → Data Collection → Data Cleaning → Exploratory Analysis → Modeling → Deployment → Monitoring
Most beginners assume modeling is where the magic happens. Reality check: you’ll spend 60-80% of your time on data cleaning and preparation. Messy data is the norm, not the exception.
What are the Core Components of Data Science?
The core components of Data Science work together to turn raw data into meaningful insights. Here are the main ones explained simply:
1. Mathematics & Statistics
This is the foundation of Data Science. It helps in understanding data patterns, probability, trends, and relationships. Concepts like linear algebra, probability, hypothesis testing, and regression are essential for analyzing data and building models.
2. Programming & Computer Science
Programming is used to work with data and build models. Languages like Python, R, and SQL help in data manipulation, automation, and the implementation of algorithms. Computer science concepts also help in handling large datasets efficiently.
3. Data Handling & Data Engineering
This component focuses on collecting, storing, and managing large amounts of data. It includes databases, data pipelines, data cleaning, and big data tools like Hadoop and Spark.
4. Machine Learning
Machine learning is a key part of Data Science that allows systems to learn from data and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. Innovators like Andrew Ng, Yann LeCun, and Fei-Fei Li have played a major role in developing modern AI and deep learning.
He proves how data-driven models can transform industries and everyday life. It is widely used in applications like recommendation systems, fraud detection, image recognition, and natural language processing
5. Domain Knowledge
Understanding the industry or field (finance, healthcare, marketing, etc.) is crucial. It helps data scientists ask the right questions and interpret results correctly.
6. Data Visualization & Communication
Insights are only useful if they can be understood. Visualization tools and storytelling skills help explain complex data in a simple and meaningful way to stakeholders.
Career Path of Data Science
Here are the details of the Data Science career path:
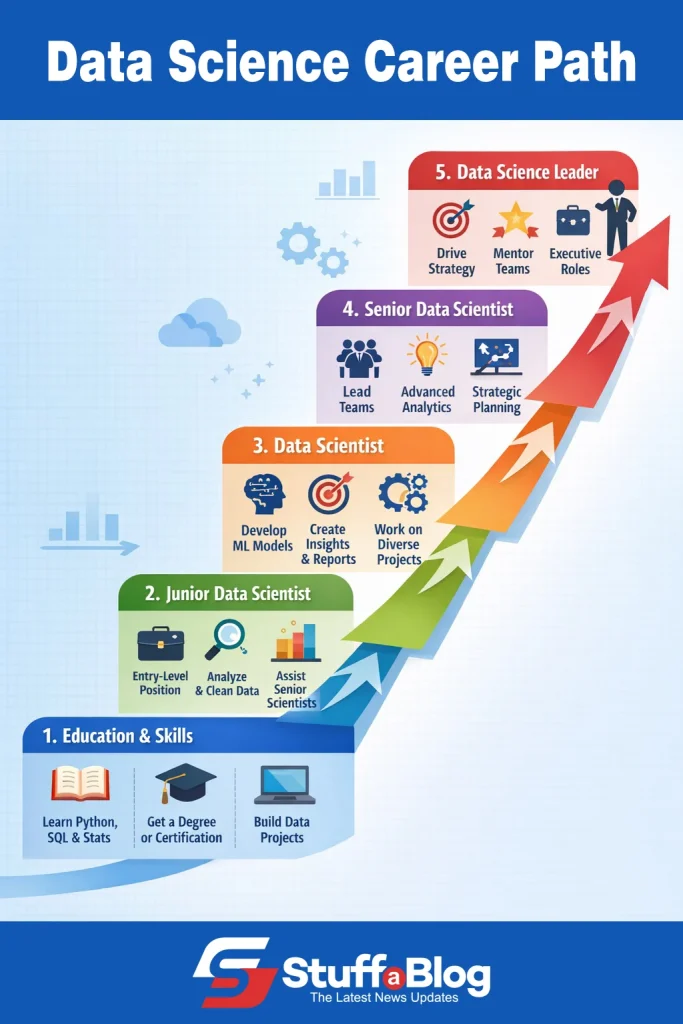
1. Educational Background and Certifications
While a degree in Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, or Engineering is helpful, many data scientists also come from non-traditional backgrounds if they develop the right skills.
Popular certifications include:
- Google Data Analytics Certificate
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate
- Microsoft Certified: Data Scientist Associate
- Certified Analytics Professional (CAP)
2. Entry-Level Roles
At the start, most professionals take on junior or assistant roles that focus on learning the basics of data handling and analysis:
- Data Analyst: Works on collecting, cleaning, and visualizing data to provide insights. Uses tools like Excel, SQL, Tableau, and Python.
- Junior Data Scientist: Assists in building models, analyzing data patterns, and supporting senior data scientists.
These roles help beginners understand data workflows and gain practical experience with real datasets.
3. Mid-Level Roles
With experience (2–5 years), professionals move into more specialized and impactful roles:
- Data Scientist: Independently builds predictive models, conducts advanced analysis, and provides actionable insights. Requires strong programming, statistics, and machine learning skills.
- Machine Learning Engineer: Focuses on implementing and optimizing machine learning models for production. Works closely with Artificial Intelligence systems and big data pipelines.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Analyst: Translates complex data into business strategies and dashboards. Often works closely with management to guide decision-making.
At this stage, professionals are expected to handle end-to-end projects and contribute to business strategy.
4. Senior-Level Roles
After gaining 5–10 years of experience, data professionals can advance into leadership and strategic roles:
- Senior Data Scientist: Leads data projects, mentors junior members, and ensures models align with business goals.
- Data Science Manager / Lead: Manages a team of data scientists and analysts, sets project priorities, and collaborates with other departments.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): A strategic role responsible for the organization’s entire data strategy, governance, and analytics initiatives.
These roles combine technical expertise with leadership and business acumen.
Key Skills Required for Data Science
- Programming Skills: Knowledge of languages like Python, R, and SQL is essential for analyzing data, building models, and automating tasks.
- Statistics and Mathematics: Understanding probability, regression, hypothesis testing, and linear algebra helps in analyzing data patterns and building predictive models.
- Data Wrangling & Cleaning: Ability to handle missing, inconsistent, or messy data and transform it into a usable format for analysis.
- Machine Learning & AI: Knowledge of algorithms and frameworks for predictive modeling, classification, clustering, and neural networks is important for advanced data projects.
- Data Visualization: Skills in Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib, or Seaborn help present data insights in a clear and understandable way for stakeholders.
- Analytical Thinking & Problem-Solving: The ability to analyze complex problems, identify trends, and extract meaningful insights from data.
- Domain Knowledge: Understanding the industry or business context ensures data insights are practical and actionable.
How Much Do Data Scientists Earn?
Data Science is one of the most in-demand and well-paying careers today. The salary of a Data Scientist can vary depending on experience, location, industry, and the company.
- Entry-Level: Freshers or junior data scientists can expect around $60,000 to $80,000 per year.
- Mid-Level: With 2–5 years of experience, salaries often range between $90,000 to $120,000 per year.
- Senior-Level: Experienced data scientists, team leads, or managers can earn $120,000 or more annually, sometimes reaching six figures in top tech companies.
For example, at major tech companies like Meta, data scientists receive highly competitive compensation packages. You can check my article on Data Scientist Salary to see how salaries vary with experience and role.
Popular Tools Used in Data Science
Data Science is powered by a wide range of tools that help professionals collect, clean, analyze, visualize, and model data. Here’s a breakdown of the most popular tools and their uses:
1. Python
Python is the most widely used programming language in Data Science due to its simplicity and versatility. It has powerful libraries such as Pandas (for data manipulation), NumPy (for numerical computing), Matplotlib and Seaborn (for visualization), and Scikit-learn (for machine learning). Python is beginner-friendly and can handle everything from simple analysis to complex AI projects.
2. R
R is a programming language specifically designed for statistical computing and graphics. It is highly effective for data analysis, hypothesis testing, and advanced statistical modeling. It also offers visualization libraries like ggplot2 for creating professional charts. R is commonly used in research, healthcare, and finance.
3. SQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is essential for working with databases. Data scientists use SQL to extract, filter, and manipulate data from relational databases. It is particularly useful for handling large datasets efficiently and preparing data for analysis.
4. Tableau
Tableau is a leading data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports. It helps data scientists and business professionals present insights in a clear, visual way that is easy for decision-makers to understand.
5. Power BI
Power BI is Microsoft’s data visualization and business intelligence tool. It is used to create interactive reports, dashboards, and data-driven storytelling. It integrates well with Excel and other Microsoft products, making it ideal for enterprise use.
6. Jupyter Notebook & Google Colab
These are interactive coding environments that allow data scientists to write code, document their process, and visualize results in one place. Jupyter Notebook is widely used locally, while Google Colab provides a cloud-based platform to code in Python without installation.
7. Machine Learning & AI Libraries
- Scikit-learn: Provides easy-to-use machine learning algorithms for classification, regression, and clustering.
- TensorFlow & Keras: Frameworks for deep learning and neural networks, useful for AI applications like image recognition and natural language processing.
- PyTorch: Another popular deep learning library, preferred for flexibility and research-oriented projects.
8. Big Data Tools
- Hadoop: An open-source framework for storing and processing large datasets across multiple servers.
- Apache Spark: Enables fast processing of large-scale data and supports machine learning and real-time analytics.
- Kafka: Handles real-time data streams and ensures data is efficiently processed across systems.
Real-World Use Cases of Data Science
Here are some of the most common and impactful use cases:
1. Healthcare
Data Science is transforming healthcare by enabling predictive analytics, diagnosis, and personalized treatment.
- Predicting diseases like diabetes or cancer early using patient data.
- Monitoring patient vitals in real-time through wearable devices.
- Optimizing hospital resource allocation and improving patient care.
Important Note
Example: AI models can analyze thousands of medical images to detect tumors faster and more accurately than traditional methods.
2. Finance & Banking
In finance, Data Science is used for risk management, fraud detection, and investment analysis.
- Detecting unusual transactions to prevent fraud.
- Predicting stock trends and market behavior.
- Assessing the creditworthiness of loan applicants using historical data.
Important Note
Example: Banks use machine learning models to flag fraudulent credit card activity instantly.
3. Marketing & E-Commerce
Data Science helps businesses understand customers and improve sales.
- Personalized product recommendations (like Netflix or Amazon).
- Analyzing customer behavior to optimize marketing campaigns.
- Predicting customer churn and retention strategies.
Example: Netflix uses data on viewing habits to suggest shows you’re likely to watch next.
4. Retail & Supply Chain
Retailers use Data Science to optimize inventory, pricing, and logistics.
- Forecasting product demand to avoid overstock or shortages.
- Dynamic pricing based on market trends and customer behavior.
- Efficient supply chain management using predictive analytics.
Important Note
Example: Walmart analyzes sales data to decide how much stock each store needs daily.
5. Technology & Artificial Intelligence
Tech companies use Data Science to build smarter AI systems and improve user experience.
- Voice assistants like Alexa or Siri use NLP (Natural Language Processing) to understand commands.
- Image recognition for social media tagging or security.
- Autonomous vehicles rely on real-time data analysis for navigation.
Important Note
Example: Tesla cars use data from millions of miles driven to improve self-driving algorithms.
6. Education
Educational platforms use Data Science to personalize learning and improve student performance.
- Tracking student progress and predicting areas where help is needed.
- Recommending courses based on learning patterns.
- Improving curriculum design using data analytics.
Important Note
Example: Online learning platforms like Coursera use analytics to suggest courses and learning paths for students.
How to Start a Career in Data Science
Here’s a step-by-step roadmap to help beginners build a strong foundation and grow into professional roles:
1. Build a Strong Educational Foundation
- Formal Education: A degree in Computer Science, Statistics, Mathematics, Engineering, or Data Science provides a strong base.
- Alternative Routes: Many successful data scientists come from non-traditional backgrounds if they gain the right skills.
Focus on subjects like statistics, probability, linear algebra, programming, and data analysis.
2. Learn Programming & Analytical Tools
- Start with Python or R for data analysis and machine learning.
- Learn SQL to handle databases efficiently.
- Explore Excel for basic data cleaning and analysis.
Tip: Focus on practical applications by solving real datasets instead of only theoretical learning.
3. Master Statistics and Mathematics
A good understanding of statistics, probability, and linear algebra is essential for analyzing data and building predictive models.
Key areas to focus on:
- Hypothesis testing
- Regression analysis
- Probability distributions
- Matrix operations for machine learning
4. Learn Machine Learning & AI Basics
- Start with simple machine learning algorithms like linear regression, decision trees, and clustering.
- Gradually explore deep learning, neural networks, and AI applications.
- Use libraries like Scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and Keras.
Tip: Implement projects to understand how algorithms work in real scenarios.
5. Gain Experience with Projects
- Work on real datasets from platforms like Kaggle, UCI Machine Learning Repository, or Google Dataset Search.
- Projects can include:
- Predicting customer churn
- Analyzing sales trends
- Building recommendation systems
Practical experience helps build a portfolio, which is crucial when applying for jobs.
6. Learn Data Visualization & Communication
- Tools like Tableau, Power BI, Matplotlib, and Seaborn help present insights clearly.
- Focus on storytelling with data — being able to explain results to non-technical stakeholders is a highly valued skill.
7. Earn Certifications & Online Courses
Certifications show employers that you have verified skills:
- Google Data Analytics Certificate
- IBM Data Science Professional Certificate
- Microsoft Certified: Data Scientist Associate
- Coursera & Udemy Data Science Courses
8. Apply for Internships or Entry-Level Roles
- Start as a Data Analyst, Junior Data Scientist, or Business Intelligence Analyst.
- Focus on learning how data is collected, cleaned, analyzed, and used in business decisions.
- Networking and LinkedIn connections can help you find opportunities.
Final Thoughts
Data Science is all about turning raw data into useful insights that help businesses, organizations, and even everyday users make better decisions. It is used in fields like healthcare, finance, marketing, and technology.
If you learn the right skills, use the right tools, and gain experience, you can start a career in Data Science. With endless opportunities and a growing demand for skilled professionals, Data Science is a field where you can learn, grow, and make a real difference in the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Data Science helps businesses and organizations make smarter decisions, improve efficiency, predict future trends, and solve real-world problems using data.
Yes, coding is essential in Data Science. Languages like Python, R, and SQL are used to analyze data, build models, and automate tasks.
The salary depends on experience and location. Entry-level data scientists can earn around $60,000–$80,000 per year, while experienced professionals can earn $120,000 or more annually.
Data Science can be challenging at first because it combines programming, statistics, and problem-solving. However, with consistent practice, online courses, and hands-on projects, anyone can learn it step by step.










